Step 1: Create a New User
To create a new user:
1. Use the adduser command:
sudo adduser [name-of-user]For instance, create a user called user1 with:
sudo adduser user1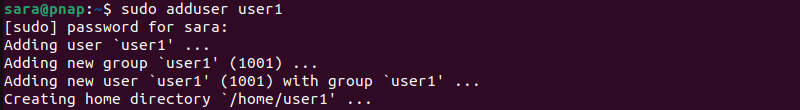
The adduser command creates a new user with a group and Home directory for that user.
2. The system prompts for a password. Enter a secure password, then retype it to confirm.
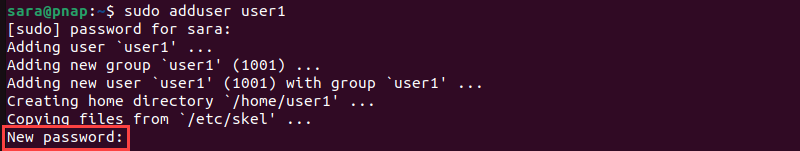
3. The system asks for additional information about the user, including name, phone numbers, etc. These fields are optional and can be skipped by pressing Enter.
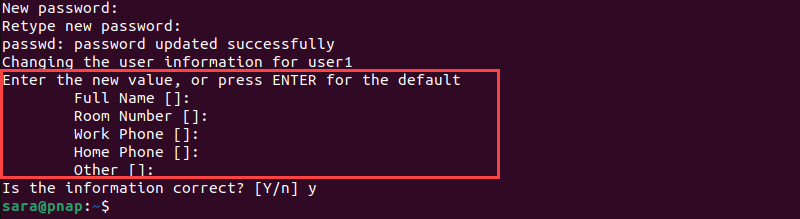
4. Type y to confirm the information and complete the settings for the new user.
Step 2: Add User to Sudoers File or Sudo Group
The sudoers file and the sudo group are related to granting users administrative privileges via the sudo command.
/etc/sudoers is a configuration file that specifies which users or groups can use sudo for administrative tasks. It defines permissions, such as command execution and password requirements.
On the other hand, the sudo group is created specifically to manage sudo privileges. Users added to this group gain sudo access to run commands with elevated permissions using sudo.
To grant users sudo permission without editing the sudoers file, add them to the sudo group with the usermod command:
sudo usermod -aG sudo [name-of-user]For example, grant user1 sudo privileges with:
sudo usermod -aG sudo user1The command has no output, but the -aG option tells the system to append the user to the specified group.
Step 3: Verify User Belongs to Sudo Group
To confirm user1 belongs to the sudoers group, view the groups the user belongs to:
groups user1
The system responds by listing the username and all groups it belongs to.
Step 4: Verify Sudo Access
To verify sudo access, take the following steps:
1. Switch users with the su command. For example:
su - user1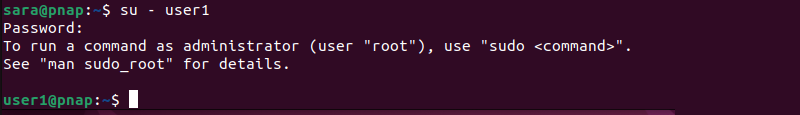
Enter the password when prompted.
2. Run a command that requires elevated privileges. For instance, list the /root directory contents using the ls command with sudo:
sudo ls /root


